This section describes the benefits of intra-group queuing.
Intra-group queuing removes the need to define channels between queue managers in a queue-sharing group.
Because there are no channels defined between queue managers in a queue-sharing group, there is no requirement for channel administration.
Because there is only one IGQ agent needed for the delivery of a message to a target queue (instead of two intermediate sender and receiver agents), the delivery of messages using intra-group queuing can be less expensive than the delivery of messages using channels. In intra-group queuing there is only a receiving component, because the need for the sending component has been removed. This saving is because the message is available to the IGQ agent at the destination queue manager for delivery to the destination queue once the put operation at the local queue manager has completed and, in the case of messages put in syncpoint scope, committed.
Applications external to a queue-sharing group can deliver messages to a queue residing on any queue manager in the queue-sharing group, while being connected only to a particular queue manager in the queue-sharing group. This is because messages arriving on a receiver channel, destined for a queue on a remote queue manager, can be transparently sent to the destination queue using intra-group queuing. This facility allows applications to be deployed among the queue-sharing group without the need to change any systems that are external to the queue-sharing group.
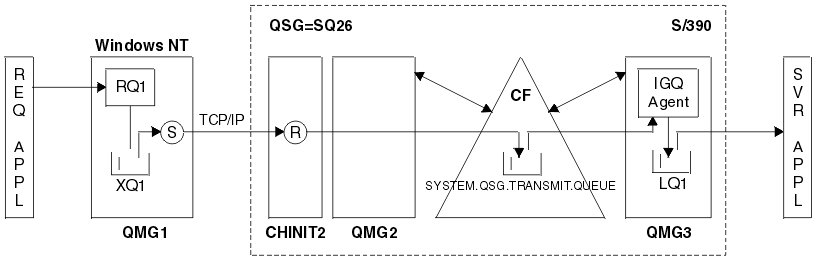
A typical configuration is illustrated by the following diagram, in which:
Figure 92. An example of migration support
 |
The flow of operations is as follows:
The above diagram also illustrates the transparent delivery of messages when multi-hopping between queue managers in a queue-sharing group. Messages arriving on a given queue manager within the queue-sharing group, but destined for a queue on another queue manager in the queue-sharing group, can be easily transmitted to the destination queue on the destination queue manager, using intra-group queuing.