The channel control function provides facilities for you to define, monitor, and control channels. Commands are issued through panels, programs, or from a command line to the channel control function. The panel interface also displays channel status and channel definition data.
The commands fall into the following groups:
Channel administration commands deal with the definitions of the channels. They enable you to:
Channel control commands manage the operation of the channels. They enable you to:
Channel monitoring displays the state of channels, for example:
Before trying to start a message channel or MQI channel, you must make sure that all the attributes of the local and remote channel definitions are correct and compatible. Chapter 6, Channel attributes describes the channel definitions and attributes.
Although you set up explicit channel definitions, the channel negotiations carried out when a channel starts up may override one or other of the values defined. This is quite normal, and transparent, and has been arranged like this so that otherwise incompatible definitions can work together.
In WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, and Windows systems, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, if there is no appropriate channel definition, then for a receiver or server-connection channel that has auto-definition enabled, a definition is created automatically. The definition is created using:
The description is then checked to determine whether it has been altered by an auto-definition exit or because the model definition has been changed. If the first 44 characters are still "Auto-defined by" followed by 29 blanks, the queue manager name is added. If the final 20 characters are still all blanks the local time and date are added.
Once the definition has been created and stored the channel start proceeds as though the definition had always existed. The batch size, transmission size, and message size are negotiated with the partner.
Before a message channel can be started, both ends must be defined (or enabled for auto-definition) at their respective queue managers. The transmission queue it is to serve must be defined to the queue manager at the sending end, and the communication link must be defined and available. In addition, it may be necessary for you to prepare other WebSphere MQ objects, such as remote queue definitions, queue manager alias definitions, and reply-to queue alias definitions, so as to implement the scenarios described in Chapter 2, Making your applications communicate.
For information about MQI channels, see the WebSphere MQ Clients book.
It is possible to define more than one channel per transmission queue, but only one of these channels can be active at any one time. This is recommended for the provision of alternative routes between queue managers for traffic balancing and link failure corrective action.
A channel can be caused to start transmitting messages in one of four ways. It can be:
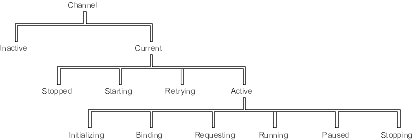
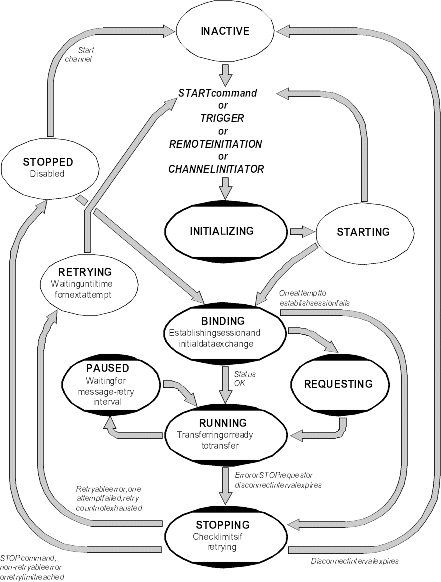
Figure 29 shows the hierarchy of all possible channel states, and Figure 30 shows the links between them. These apply to all types of message channel. On WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, and Windows systems, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, these states apply also to server-connection channels.
 |
The channel is "current" if it is in any state other than inactive. A current channel is "active" unless it is in RETRYING, STOPPED, or STARTING state.
Figure 30. Flows between channel states
 |
Notes:
You can specify the maximum number of channels that can be current at one time. This is the number of channels that have entries in the channel status table, including channels that are retrying and channels that are disabled (that is, stopped). Specify this in the channel initiator parameter module for z/OS, the queue manager initialization file for iSeries, the queue manager configuration file for OS/2, Compaq NonStop Kernel, and UNIX systems, or the registry for Windows. For more information about the values you set using the initialization or the configuration file see Appendix C, Configuration file stanzas for distributed queuing. For more information about specifying the maximum number of channels, see the WebSphere MQ System Administration Guide for WebSphere MQ for AIX, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, and Windows systems, and MQSeries V5.1 for Compaq Tru64 UNIX, and OS/2 Warp, the WebSphere MQ for iSeries V5.3 System Administration book for WebSphere MQ for iSeries, or the WebSphere MQ for z/OS Concepts and Planning Guide for information relating to your platform.
Notes:
You can also specify the maximum number of active channels (except on WebSphere MQ for z/OS using CICS). You can do this to prevent your system being overloaded by a large number of starting channels. If you use this method, you should set the disconnect interval attribute to a low value to allow waiting channels to start as soon as other channels terminate.
Each time a channel that is retrying attempts to establish connection with its partner, it must become an active channel. If the attempt fails, it remains a current channel that is not active, until it is time for the next attempt. The number of times that a channel will retry, and how often, is determined by the retry count and retry interval channel attributes. There are short and long values for both these attributes. See Chapter 6, Channel attributes for more information.
When a channel has to become an active channel (because a START command has been issued, or because it has been triggered, or because it is time for another retry attempt), but is unable to do so because the number of active channels is already at the maximum value, the channel waits until one of the active slots is freed by another channel instance ceasing to be active. If, however, a channel is starting because it is being initiated remotely, and there are no active slots available for it at that time, the remote initiation is rejected.
Whenever a channel, other than a requester channel, is attempting to become active, it goes into the STARTING state. This is true even if there is an active slot immediately available, although in this case it will only be in STARTING state for a very short time. However, if the channel has to wait for an active slot, it is in STARTING state while it is waiting.
Requester channels do not go into STARTING state. If a requester channel cannot start because the number of active channels is already at the limit, the channel ends abnormally.
Whenever a channel, other than a requester channel, is unable to get an active slot, and so waits for one, a message is written to the log or the z/OS console, and an event is generated. When a slot is subsequently freed and the channel is able to acquire it, another message and event are generated. Neither of these events and messages are generated if the channel is able to acquire a slot straightaway.
If a STOP CHANNEL command is issued while the channel is waiting to become active, the channel goes to STOPPED state. A Channel-Stopped event is raised as usual.
On WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, Windows systems, and z/OS, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, server-connection channels are included in the maximum number of active channels.
For more information about specifying the maximum number of active channels, see the WebSphere MQ System Administration Guide book for WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Solaris, and Windows systems, and MQSeries for Compaq Tru64 UNIX, and OS/2 Warp, the WebSphere MQ for iSeries V5.3 System Administration book for WebSphere MQ for iSeries, or the WebSphere MQ for z/OS Concepts and Planning Guide for the z/OS platform.
Errors on channels cause the channel to stop further transmissions. If the channel is a sender or server, it goes to RETRY state because it is possible that the problem may clear itself. If it cannot go to RETRY state, the channel goes to STOPPED state. For sending channels, the associated transmission queue is set to GET(DISABLED) and triggering is turned off. (A STOP command with STATUS(STOPPED) takes the side that issued it to STOPPED state; only expiry of the disconnect interval or a STOP command with STATUS(INACTIVE) will make it end normally and become inactive.) Channels that are in STOPPED state need operator intervention before they will restart (see Restarting stopped channels).
Long retry count (LONGRTY) describes how retrying works. If the error clears, the channel restarts automatically, and the transmission queue is re-enabled. If the retry limit is reached without the error clearing, the channel goes to STOPPED state. A stopped channel must be restarted manually by the operator. If the error is still present, it does not retry again. When it does start successfully, the transmission queue is re-enabled.
On WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, Windows systems, and z/OS without CICS, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, if the channel initiator or queue manager stops while a channel is in RETRYING or STOPPED status, the channel status is remembered when the channel initiator or queue manager is restarted.
On OS/2 Warp, Windows systems, iSeries, Compaq NonStop Kernel, and UNIX systems, if a channel is unable to put a message to the target queue because that queue is full or put inhibited, the channel can retry the operation a number of times (specified in the message-retry count attribute) at a given time interval (specified in the message-retry interval attribute). Alternatively, you can write your own message-retry exit that determines which circumstances cause a retry, and the number of attempts made. The channel goes to PAUSED state while waiting for the message-retry interval to finish.
See Chapter 6, Channel attributes for information about the channel attributes, and Chapter 45, Channel-exit programs for information about the message-retry
exit.
In WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, Windows systems,
and z/OS without CICS, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, you can use the
heartbeat-interval channel attribute to specify that flows are to be passed
from the sending MCA when there are no messages on the transmission
queue. This is described in Heartbeat interval (HBINT).
In WebSphere MQ for z/OS, if you are using TCP as the transport protocol,
you can also specify a value for the KeepAlive Interval channel attribute
(KAINT). You are recommended to give the KeepAliveInterval a higher
value than the heartbeat interval, and a smaller value than the disconnect
value. You can use this attribute to specify a time-out value for each
channel. This is described in KeepAlive Interval (KAINT).
In WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, Windows systems,
and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, if you are using TCP as your transport
protocol, you can set keepalive=yes in the qm.ini
file. If you specify this option, TCP periodically checks that the
other end of the connection is still available, and if it is not, the channel
is terminated.
In WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, and Windows
systems, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, if you are using TCP as your
transport protocol, the receiving end of inactive connections are also closed
if no data is received for a period of time. This period of time is
determined according to the HBINT (heartbeat interval) value.
The time-out value is set as follows:
Notes: If you have unreliable channels that are suffering from TCP errors, use
of SO_KEEPALIVE will mean that your channels are more likely to
recover.
You can specify time intervals to control the behavior of the SO_KEEPALIVE
option. When you change the time interval, only TCP/IP channels started
after the change are affected. The value that you choose for the time
interval should be less than the value of the disconnect interval for the
channel.
For more information about using the SO_KEEPALIVE option on z/OS, see WebSphere MQ for z/OS Concepts and Planning Guide .
For other platforms, see the chapter about setting up communications for your
platform in this manual.Checking that the other end of the channel is still available
If a channel suffers a communications failure, the receiver channel could be left in a 'communications receive' state. When communications are re-established the sender channel attempts to reconnect. If the remote queue manager finds that the receiver channel is already running it does not allow another version of the same receiver channel to be started. This problem requires user intervention to rectify the problem or the use of system keepalive.
The Adopt MCA function solves the problem automatically. It enables WebSphere MQ to cancel a receiver channel and to start a new one in its place.
The function can be set up with various options. For more
information see WebSphere MQ for z/OS System Setup
Guide or the appropriate equivalent publication for your
platforms.
Message channels are designed to be long-running connections between queue
managers with orderly termination controlled only by the disconnect interval
channel attribute. This mechanism works well unless the operator needs
to terminate the channel before the disconnect time interval expires.
This can occur in the following situations:
In this case, an operator command is provided to allow you to stop the
channel. The command provided varies by platform, as follows:
There are three options for stopping channels using these commands:
Note that all of these options leave the channel in a STOPPED state,
requiring operator intervention to restart it.
Stopping the channel at the sending end is quite effective but does require
operator intervention to restart. At the receiving end of the channel,
things are much more difficult because the MCA is waiting for data from the
sending side, and there is no way to initiate an orderly
termination of the channel from the receiving side; the stop command is
pending until the MCA returns from its wait for data.
Consequently there are three recommended ways of using channels, depending
upon the operational characteristics required:
Notes: Stopping and quiescing channels
When a channel goes into STOPPED state (either because you have stopped the channel manually using one of the methods given in Stopping and quiescing channels, or because of a channel error) you have to restart the channel manually.
To do this, issue one of the following commands:
For sender or server channels, when the channel entered the STOPPED state, the associated transmission queue was set to GET(DISABLED) and triggering was set off. When the start request is received, these attributes are reset automatically. On WebSphere MQ for AIX, iSeries, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, Windows systems, and z/OS without CICS, and MQSeries V5.1 for OS/2 Warp, if the channel initiator or queue manager stops while a channel is in RETRYING or STOPPED status, the channel status is remembered when the channel initiator or queue manager is restarted. On other platforms, if the channel initiator or queue manager is restarted the status is lost and you have to alter the queue attributes manually to re-enable triggering of the channel.
An in-doubt channel is a channel that is in doubt with a remote channel about which messages have been sent and received. Note the distinction between this and a queue manager being in doubt about which messages should be committed to a queue.
You can reduce the opportunity for a channel to be placed in doubt by using the Batch Heartbeat channel parameter (BATCHHB). When a value for this parameter is specified, a sender channel checks that the remote channel is still active before taking any further action. If no response is received the receiver channel is considered to be no longer active. The messages can be rolled-back, and re-routed, and the sender-channel is not put in doubt. This reduces the time when the channel could be placed in doubt to the period between the sender channel verifying that the receiver channel is still active, and verifying that the receiver channel has received the sent messages. See Chapter 6, Channel attributes for more information on the batch heartbeat parameter.
In-doubt channel problems are usually resolved automatically. Even when communication is lost, and a channel is placed in doubt with a message batch at the sender whose receipt status is unknown, the situation is resolved when communication is re-established. Sequence number and LUWID records are kept for this purpose. The channel is in doubt until LUWID information has been exchanged, and only one batch of messages can be in doubt for the channel.
You can, when necessary, resynchronize the channel manually. The term manual includes use of operators or programs that contain WebSphere MQ system management commands. The manual resynchronization process works as follows. This description uses MQSC commands, but you can also use the PCF equivalents.
DISPLAY CHSTATUS(name) SAVED CURLUWID
You can use the CONNAME and XMITQ parameters to further identify the channel.
DISPLAY CHSTATUS(name) SAVED LSTLUWID
You can use the CONNAME parameter to further identify the channel.
The commands are different because only the sending side of the channel can be in doubt. The receiving side is never in doubt.
On WebSphere MQ for iSeries, the DISPLAY CHSTATUS command can be executed from a file using the STRMQMMQSC command or the Work with MQM Channel Status CL command, WRKMQMCHST
RESOLVE CHANNEL(name) ACTION(COMMIT)
RESOLVE CHANNEL(name) ACTION(BACKOUT)
On WebSphere MQ for iSeries, you can use the Resolve MQM Channel command, RSVMQMCHL.
Once this process is complete the channel is no longer in doubt. The transmission queue can now be used by another channel, if required.
There are two distinct aspects to problem determination:
Commands and panel data must be free from errors before they are accepted for processing. Any errors found by the validation are immediately notified to the user by error messages.
Problem diagnosis begins with the interpretation of these error messages and taking the recommended corrective action.
Problems found during normal operation of the channels are notified to the system console or the system log. Problem diagnosis begins with the collection of all relevant information from the log, and continues with analysis to identify the problem.
Confirmation and error messages are returned to the terminal that initiated the commands, when possible.
Where provided, the Messages and Codes manual of the particular platform can help with the primary diagnosis of the problem.