Figure 28 shows the relationships between entities when messages are
transmitted, and shows the flow of control.
Figure 28. Distributed queue management model
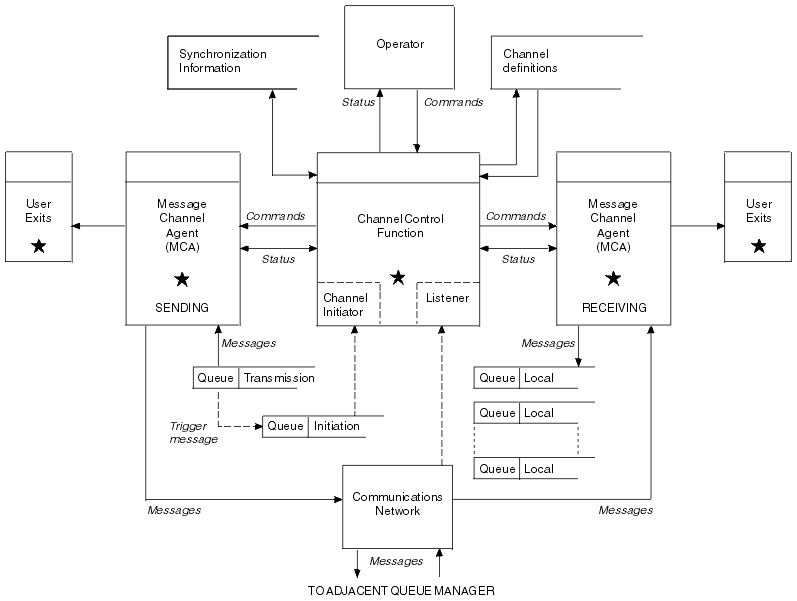
Notes:
- There is one MCA per channel, depending on the platform. There may
be one or more channel control functions for a given queue manager.
- The implementation of MCAs and channel control functions is highly
platform dependent; they may be programs or processes or threads, and
they may be a single entity or many comprising several independent or linked
parts.
- All components marked with a star can use the MQI.
An MCA receives its parameters in one of several ways:
- If started by a command, the channel name is passed in a data area.
The MCA then reads the channel definition directly to obtain its
attributes.
- For sender, and in some cases server channels, the MCA can be started
automatically by the queue manager trigger. The channel name is
retrieved from the trigger process definition, where applicable, and is passed
to the MCA. The remaining processing is the same as that described
above.
- If started remotely by a sender, server, requester, or client-connection,
the channel name is passed in the initial data from the partner message
channel agent. The MCA reads the channel definition directly to obtain
its attributes.
Certain attributes not defined in the channel definition are also
negotiable:
- Split messages
- If one end does not support this, split messages will not be sent.
- Conversion capability
- If one end cannot perform the necessary code page conversion or numeric
encoding conversion when needed, the other end must handle it. If
neither end supports it, when needed, the channel cannot start.
- Distribution list support
- If one end does not support distribution lists, the partner MCA sets a
flag in its transmission queue so that it will know to intercept messages
intended for multiple destinations.
Message channel agent programs keep records of the current sequence number
and logical unit of work number for each channel, and of the general status of
the channel. Some platforms allow you to display this status
information to help you control channels.
© IBM Corporation 2002. All Rights Reserved

